Speed and rapidity are terms used synonymously to refer to the relationship between the distance traveled and the time taken to cover it.
However, not in all cases speed and rapidity refer to the same thing. In more specialized fields, such as physics, they have slight differences.
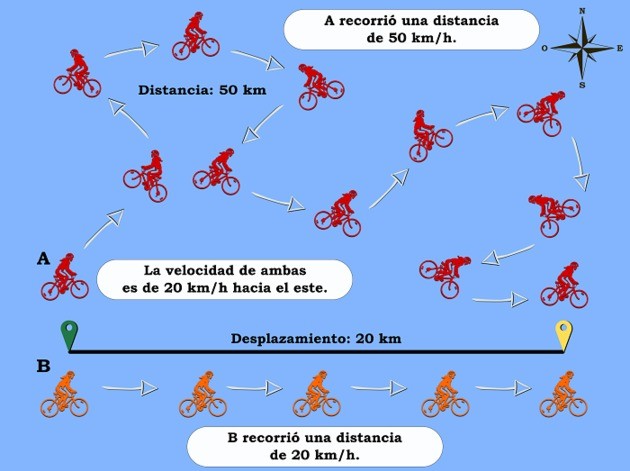
The speed refers to the distance traveled by an object in a time determined. Since this is calculated by taking the distance traveled and dividing it by the time, the speed is a magnitude scalar.
In contrast, the speed refers to the interval of time it takes for an object to move towards a address determined. Since it involves the direction or sense of motion, velocity is a magnitude vector.
|
Speed |
Speed |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
A scalar quantity representing a distance traveled by a body in a given time. |
It is a vector magnitude representing the displacement of a body in a time interval. |
|
Characteristics |
|
|
|
Calculation |
Speed = distance traveled / time elapsed. |
Velocity = displacement / elapsed time. |
|
Average |
It is obtained by dividing the distance traveled by the time elapsed. |
It is obtained by dividing the displacement by the elapsed time. |
| Magnitude | Scalar: described only with the use of numerical units. | Vector: described with the use of numerical units and direction. |
What is speed
The speed indicates the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time it took to travel it. As such, it can be measured in meters, kilometers, miles or knots (in the aquatic environment), per hour or per second.
Since speed is expressed in terms of distance and time, it is characterized as being a scalar magnitudewhich means that only the following are used to describe speed numerical units.
Since speed involves covering a distance during a time interval, it can only give a positive value.
Characteristics of speed
- Consider the distance traveled and the time elapsed.
- It is a scalar magnitude.
- The average speed results from the division between the distance and a time interval.
- It is always positive.
Average speed
Average speed refers to the total distance traveled during a given time.
For example, when Usain Bolt set the world record for the 100-meter dash in 9.58 seconds, his average speed was 10.44 meters per second.
What is speed
The speed expresses the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time it takes to travel it to a address specific.
Basically, velocity refers to the positional change of an object, from an initial reference point, to the place to which this object has moved (the end point of the motion), and to the time it has taken to do so.
Being a magnitude that also determines the direction in which the displacementvelocity is considered a magnitude of vector character.
Velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s, according to the International System of Units), by direction.
In this sense, for an object to have a constant velocity, it must move in a constant direction for a certain amount of time. Any change in direction will imply variations in speed.
Speed characteristics
- Consider the change in position of an object toward a specific direction.
- It is a vector magnitude.
- The average velocity involves the displacement between the time interval.
- It can give a positive, negative or even null (zero) value.
Average speed
The average velocity is that displacement of an object from one position to another in a given time.
Since velocity takes displacement into consideration, if an object is in the same position after a specific time interval, its velocity is null (zero). In the same way, this magnitude can even become negative.
Learn more about the Difference between distance and displacement.
Example of speed and velocity
An example to better understand the difference between velocity and speed would be the following: if an object is traveling northward at 100 kilometers per hour for one hour, it will have a speed of 100 km/h north.
On the other hand, if instead of going north, it follows a circular path at 100 km/h for one hour, finishing at the same point where it started, then we will say that its speed has been zeroalthough for this purpose he had a speed of 100 km/h.
Speed, then, would be the absolute scalar value of velocity. In this sense, if there is no direction or course, we are talking about speed, while if a direction is followed, then we are talking about velocity.
You may be interested in knowing about Scalar and vector magnitude.