/
Oral and written communication: what it is, distinctions and differences

Oral communication is a type of communication established between two or more people who exchange ideas, thoughts and emotions through spoken language. Written communication is a type of communication that allows the expression of ideas, thoughts and emotions through the…
Biome types: how many are there in the world?

The world’s biomes are communities of plants and animals characteristic of a climate. The key ingredient in recognizing a particular biome is vegetation. Biome is an extended expression of ecosystems, i.e., a biome can cover several ecosystems. The 8 main…
Methods of separation of mixtures: what are they and 12 examples?

Methods of separation of mixtures are physical techniques used to separate the components of a mixture. A mixture can be homogeneous, when its components are indistinguishable to the naked eye, or heterogeneous, when differences between its components are evident. The…
General and specific objectives: what they are and their differences

General and specific objectives are fundamental elements for the realization of academic works, such as, for example, a degree thesis. The general objective is a statement that summarizes the central idea and purpose. of a work. The specific objectives detail…
Scalar and vector magnitudes: what they are and their differences
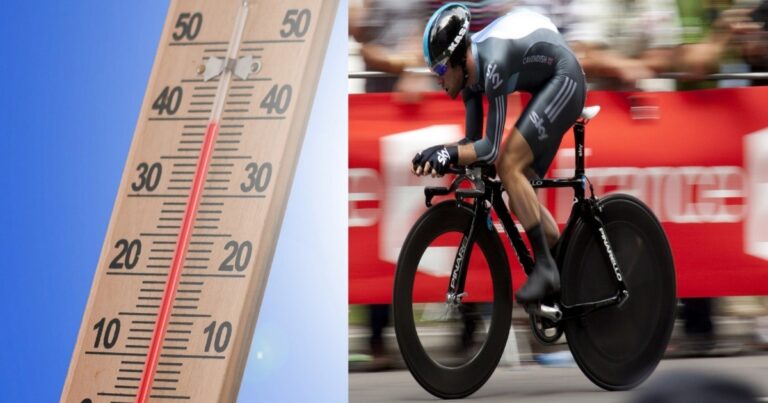
The scalar magnitude is the quantity that we can measure of a certain property that does not depend on its direction or position in space. The vector magnitude is the quantity we can measure that depends on the direction or…
Types of memory: short term, long term and sensory (with examples)

The human being has three types of memory essential: the short-term memorythe long-term memory and the sensory memory. Short-term memory is dedicated to retaining information for short periods of time. Long-term memory, on the other hand, has a greater temporality,…
