/
The types of migration that exist

Migration is the geographic displacement made by a person or group of people away from their place of origin in order to settle in a new destination, either temporarily or permanently. There are different types of migration depending on factors…
Difference between Racism, Discrimination and Prejudice

The racism is the belief that people belong to different races and that one race is superior to the others. The discrimination is the action based on prejudice and occurs when there is differential treatment of someone because he or…
Phases of mitosis: what are they and their characteristics?
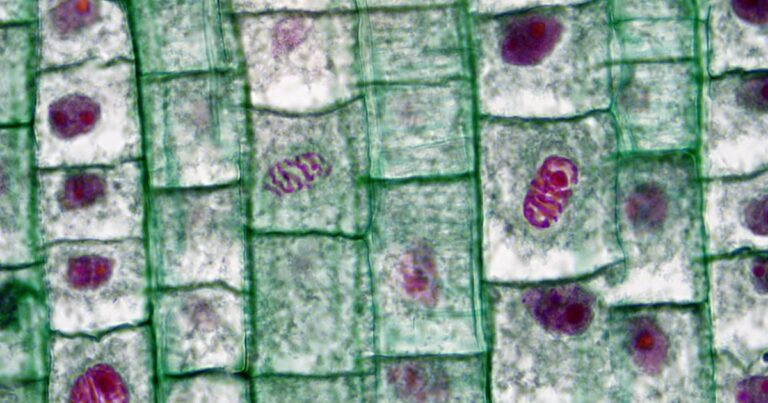
Mitosis is the sequence of events by which a eukaryotic cell (progenitor cell) produces two daughter cells with the same genetic information as the original cell. Mitosis is the stage of the cell cycle that follows interphase, where the cell…
60 Examples of acids and bases: in everyday life and with formulas

The acids are compounds that either accept electrons or donate protons (H+) in aqueous solutions and the bases are compounds that donate electrons, accept protons (H+) or release hydroxyl ions (OH-) in aqueous solutions. Here are examples of commonly used…
Difference between capitalism and socialism

The main differences between capitalism and socialism revolve around the. role of government and to the equality of economy. The main differences are presented below: Capitalism Socialism Definition A theory or system of social organization based on the. free market…
Difference between cost and expense

Cost is any disbursement made by a company to maintain its production process of goods or services (purchases of raw materials, transportation of products, etc.). Expense are all disbursements or payments made by the company to produce the product or…
