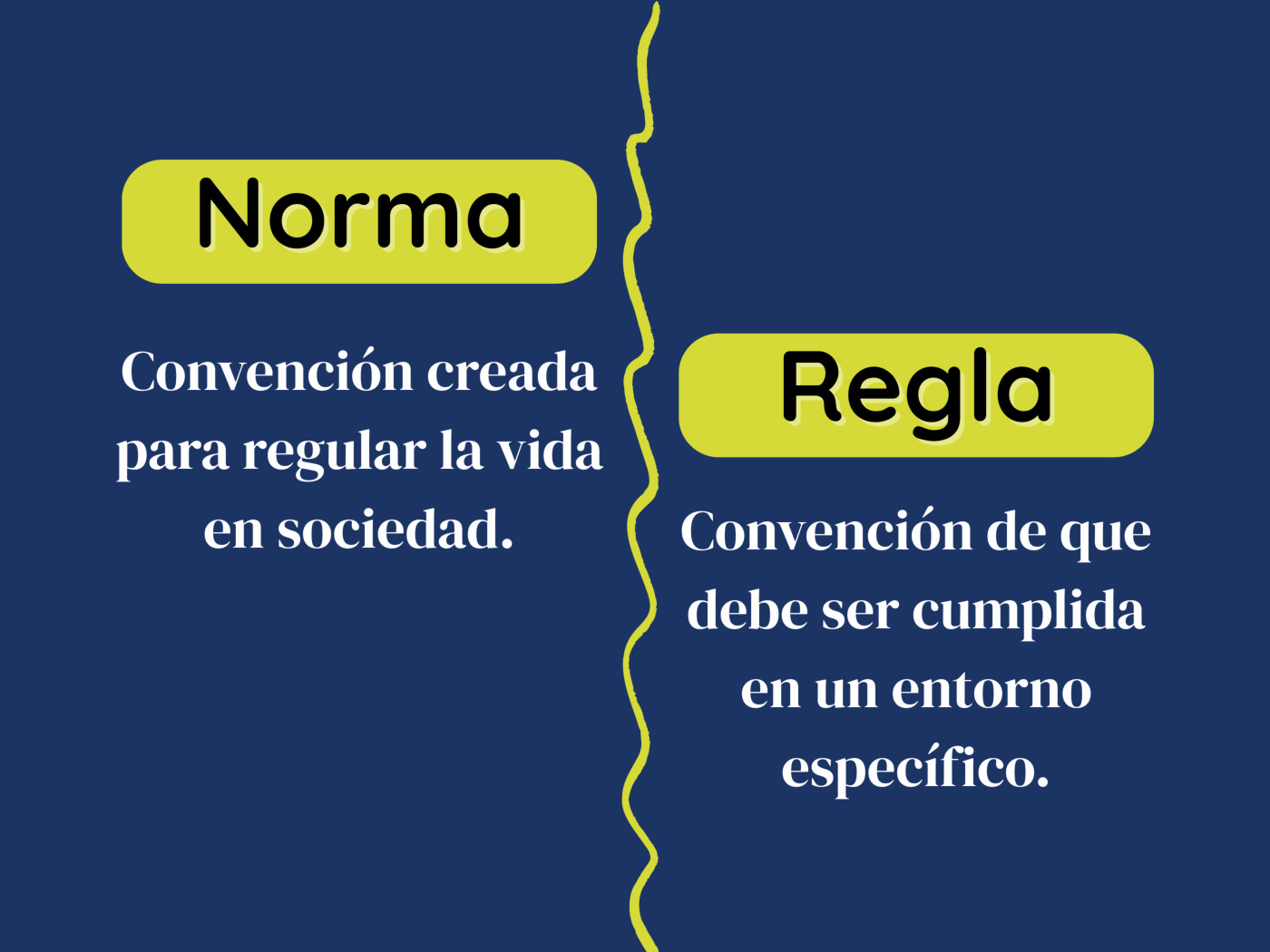
A norm is a collective consensus, created to regulate the behavior of individuals in a society.
A rule is a formal guideline of a social or legal nature, the non-compliance with which is morally or legally penalized.
| Rule | Rule | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Convention created to regulate life in society. | Convention that must be complied with in a specific environment. |
|
Type of agreement |
Social |
Social. Legal. |
| Form of transmission | Oral. | Written. |
|
Type of sanction |
Moral. |
Moral. Legal. |
| Example |
Punctuality is considered a social agreement. Failure to comply may imply a moral sanction. |
One of the rules in companies is working hours. By not complying with them, what was agreed in the contract is not respected and may imply a sanction or dismissal. |
What is a rule?
A standard refers to all the guidelines or guidelines that govern the conduct or behavior of a collectivity, such as a company, a community or society in general.
Norms are social agreements, therefore, individuals are expected to respect such agreements. Hence, some norms may have legal and juridical relevance over time.
In addition, norms also imply moral aspects of society such as fairness, respect or honesty.
Non-compliance or violation of a norm does not carry a legal sanction (unless the norm has become a rule), but it does imply social disapproval.
For example, it is a norm to be silent in hospital waiting rooms. Although compliance with the norm is expected, speaking in such places does not imply a breach of the law.
In many cases, the rules are not written, but are part of oral tradition and are enforced by social convention.
What is a rule?
The rule, on the other hand, is much more specific than the norm. Rules tell us what must be done and what is not allowed, as well as the respective sanctions in case of non-compliance.
In this sense, rules can refer to more specific issues in a social or organizational environment. In some cases they derive from general norms.
Usually rules are recorded in writing, and may be institutionalized before formal bodies, such as traffic laws, the penal code, etc.
In this sense, rules regulate life in society more strictly than norms, since their omission or non-compliance can lead to moral sanctions or even imprisonment, depending on the environment, the severity and the type of sanction agreed upon according to the offense.
See also: