The power supply is the action of living organisms of ingesting any type of food, solid or liquid, to satisfy their biological needs.
The nutrition is the obtaining and utilization of those components or nutrients present in food, which are vital for the growth and/or life of the organism.
The difference between feeding and nutrition is that the former action refers to the actions involved with obtaining and choosing food.and the second involves the food processing and digestion inside the organism.
Feeding generates a process of nutrition, and nutrition depends on feeding to take place.
| Differences | Feeding | Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is the procurement and selection of food to be ingested. | It is the process of digesting the food consumed to obtain its nutrients. |
| Characteristics |
|
|
| Types |
|
|
What is nutrition?
Nourishment is the procurement, selection and preparation of food. for the purpose of ingestion. In the case of humans, food can be natural or man-made, solid or liquid, and may or may not require prior processing (cleaning, boiling, cooking, etc.).
Eating is an act that depends on many factors:
- learning,
- the geographical environment,
- the social group,
- customs,
- socioeconomic factors,
- personal preferences,
- health conditions, etc.
Hence, although it is a universal act, it is not performed in the same way all over the world, not even within the same social group.
On the other hand, eating is an individual and voluntary act, since each person can decide how and when to eat.
It is important to note that the terms diet and food refer to the act of choosing the foods to be consumed. When the food selection has to be specific (either because of illness, as part of a weight loss program, food allergies, etc.), it is then a food plan.
Types of food
Since the procurement and selection of food depends on multiple factors, feeding types can vary widely. However, there are general classifications that allow us to identify the most popular types of feeding.
Balanced feeding
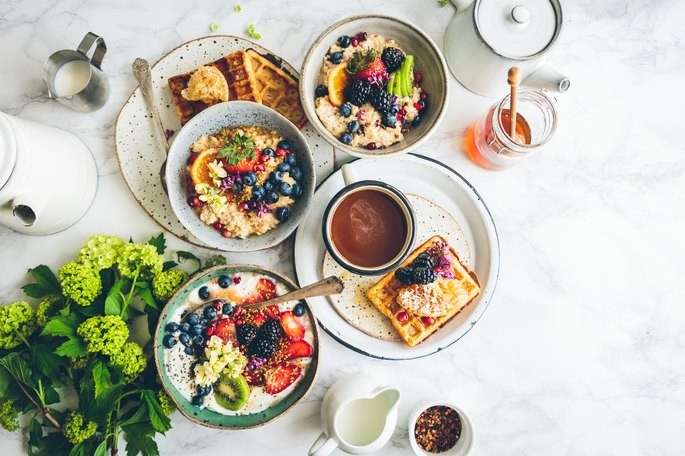

It includes a selection of foods from all food groups (milk, meats, vegetables, vegetables, fruits, cereals and fats) in moderate amounts, which should be present in all meals taken.
Vegetarian diet
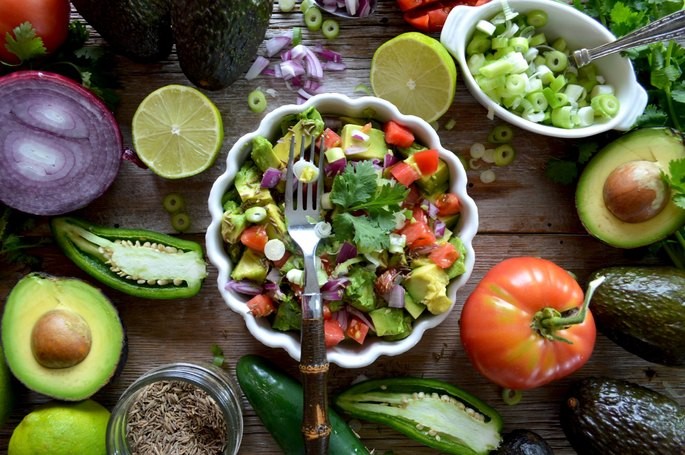

It is a type of diet based on the consumption of vegetables, legumes, cereals, fruits and fats of non-animal origin. Within vegetarianism there are some subclassifications, such as:
- Ovolactovegetarianismincludes eggs and dairy products.
- Lacto-vegetarianismincludes milk and other dairy products.
- Veganism: excludes any food of animal origin. More than a type of diet, it is a practice in which the consumption and use of products made from animals is avoided.
Mediterranean diet
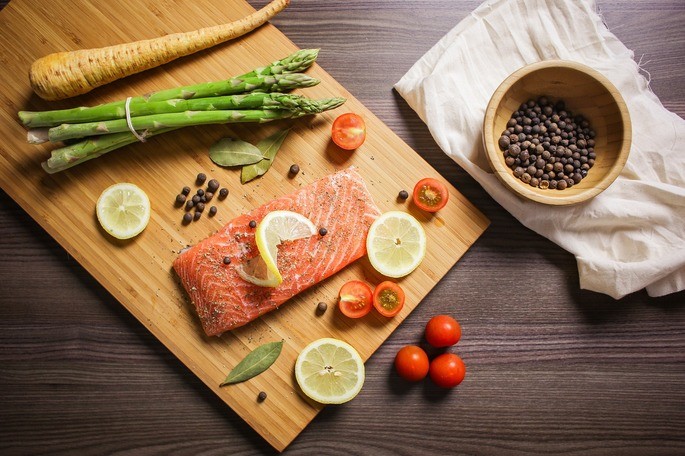

Also known as the “Mediterranean diet”, this is a selection of foods based on the eating habits of the inhabitants of the Mediterranean region (Spain, Portugal, Italy, France, Greece, Morocco, Cyprus and Croatia).
This type of diet includes large amounts of vegetables, grains, fruits, legumes, and monounsaturated fats (such as those found in oily fish and nuts), while the consumption of red meat is reduced.
You may be interested to see also Advantages and disadvantages of transgenic foods.
What is nutrition?
Nutrition is the process by which living organisms transform food into energy and matter.in order to fulfill their vital functions. This process is carried out after digesting food to obtain the nutrients they need.
Nutrition includes the absorption of food, its digestion, metabolization and excretion of wastes or elements that are not nutritional or that have already been used by the organism.
For an organism to be able to nourish itself, in the sense that it can obtain the energy it needs, it is required that the selection of food is appropriate for its needs, therefore, the type of food has a direct influence on the quality of nutrition,
However, nutrition is a biological, physiological and involuntary process.Therefore, it will take place once the food is ingested and independently of its type, quality or quantity.
Types of nutrition
Depending on their type of nutrition, living things can be autotrophic or heterotrophic, depending on their primary source of food.
Autotrophic nutrition

It is the absorption of nutrients from inorganic substances. Autotrophs produce their own food from carbon dioxide, which they obtain in one of these processes:
- Photosynthesisis the obtaining of organic matter from light energy. Most plants are photosynthetic autotrophs.
- Chemosynthesisin this case, nutrients are obtained after a process of oxidation-reduction of inorganic compounds. Bacteria, for example, are chemosynthetic autotrophs.
Heterotrophic nutrition
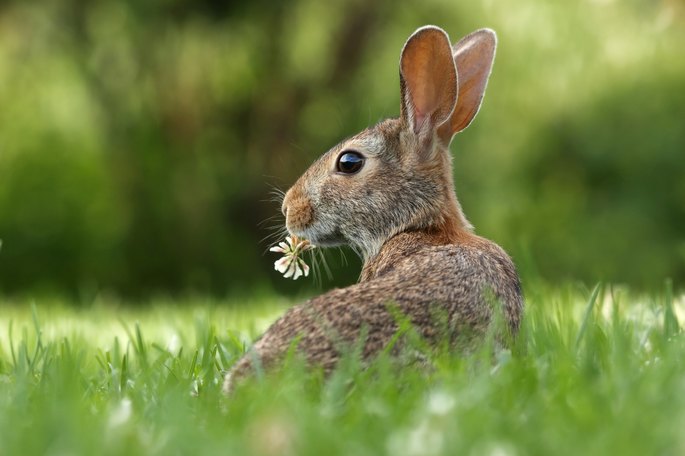

The process of synthesizing nutrients from organic substances. Heterotrophs cannot produce their own food, so they depend on other organisms for nutrition, either autotrophs or heterotrophs.
Humans, animals, fungi and some microorganisms are heterotrophs.And in turn, they are subclassified into three types.
- HerbivoresHerbivores: refers to living beings that only feed on plants. In this case, their digestive system cannot process other types of organic matter. They depend directly on autotrophs, which provide them with food by converting inorganic matter into organic matter. Rabbits, horses and elephants are examples of herbivorous animals.
- CarnivoresCarnivores: organisms that feed only on meat. In order to do so, they evolved to develop teeth, which allow them to obtain and grind food. coyote, dolphin and crocodile are some carnivorous animals.
- Omnivores: in this case, the food source is herbivorous and carnivorous. They are not adapted to feed on plants or meat exclusively, so they combine both sources. Mammals (including humans), birds and some species of fish and reptiles are omnivores.
You may be interested to see also: