The main differences between capitalism and socialism revolve around the. role of government and to the equality of economy.
The main differences are presented below:
| Capitalism | Socialism | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A theory or system of social organization based on the. free market and in privatization, where ownership is attributed to individuals. The capitalist system defends the economic freedomconsumer choice and economic growth. |
A theory or system of social organization based on the exploration of most goods in common, with ownership attributed to the workers. In socialism, the state controls the economyand is responsible for reducing social inequality through programs that benefit the poor. |
| Philosophy | The means of production are privately owned, being operated and traded to generate profits for private owners or shareholders. It has emphasis on individual profit and not on workers or society as a whole. |
Idea of transformation of society through balanced distribution of property and wealth, decreasing the gap between rich and poor. Profits are distributed among society to supplement wages. |
| Ideas | Capitalism opposes government intervention in the economy because capitalists believe it introduces inefficiencies. A free market produces the best economic outcome for society. |
All individuals should have access to basic consumer goods and public goods. Large-scale industries are collective goods and, therefore, the return from these industries should benefit society as a whole. |
| Leading advocates | Richard Cantillon, Adam Smith. | Karl Marx, Friedrich Engels, Lenin. |
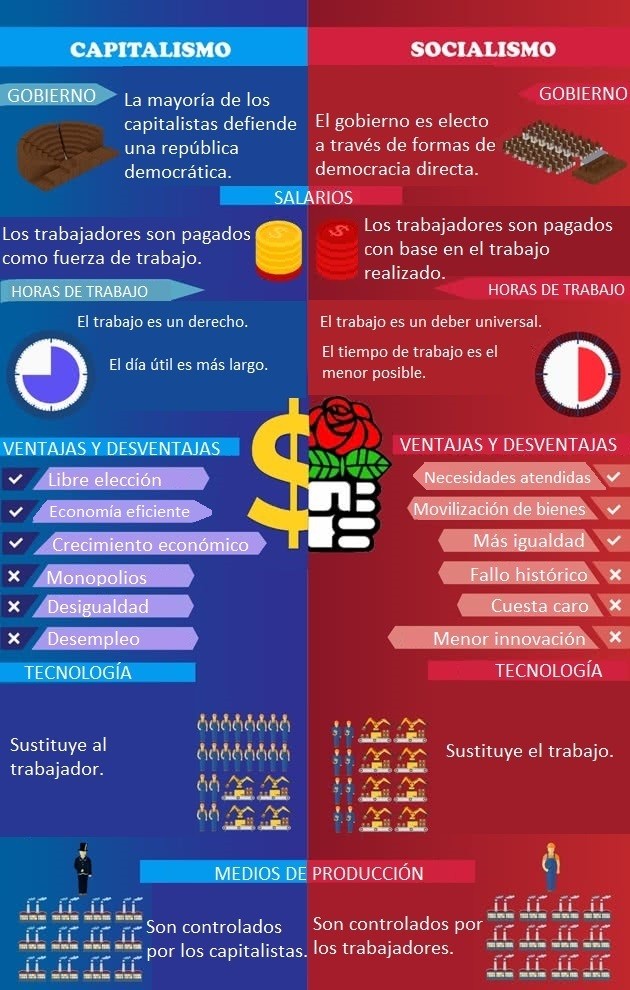
| Political system | It can coexist with a variety of political systems, including dictatorship, democratic republic, anarchism and direct democracy. The majority of capitalists advocate a democratic republic. |
It can coexist with different political systems. The majority of socialists defend the participatory democracy. |
| Economic system | Market-based economy with private or corporate ownership of the means of production. Goods and services are produced for profit and that profit is reinvested in the economy to fuel economic growth. |
The means of production are owned by public or cooperative enterprises, and individuals are compensated based on the principle of individual contribution. Production can be coordinated through economic or market planning. |
| Social structure | Classes exist according to their relation to capital: capitalists own part of the means of production and derive their income that way, while the working class depends on wages. | Class differences are diminished. Status derives in political distinctions, rather than class distinctions. |
| Religion | Freedom of religion. | Freedom of religion. |
| Private property | Private ownership of capital and other property is the dominant form of property. Public ownership and state ownership play a secondary role, and there may also be some collective ownership in the economy. |
There are two types of property: personal property (houses, clothes, etc.) and public property, which includes factories and means of production owned by the state, but under the control of the workers. |
| Free choice | All individuals make choices for themselves, and must live with the consequences of their actions. Freedom of choice allows consumers to drive the economy. |
Religion, employment, and marriage are up to the individual. Education is compulsory. |
| Economic coordination | The market determines investment, production and distribution decisions. Markets may be free markets, regulated markets, or may be combined with a degree of state-directed economic planning within private enterprises. |
Socialism depends on planning to determine investment and production decisions. Planning can be centralized or decentralized. |
| Examples | The modern world economy operates largely according to the principles of capitalism. The United States is widely considered the bastion of capitalism, however, every developed country has some programs that are socialist. |
Socialist countries are those whose constitutions include statements about protecting the working class, such as Cuba, North Korea, China, Laos and Vietnam. |
| Ownership structure | The means of production are privately owned and operated for private profit. This encourages producers to engage in economic activities. Enterprises may be owned by individuals, worker cooperatives, or shareholders. |
The means of production are socially owned with the profit produced going to society as a whole (in public ownership models) or to all staff members of the enterprise (in cooperative ownership models). |
| Political movements | Classical liberalism, social liberalism, libertarianism, neoliberalism, modern social democracy and anarchism. | Democratic socialism, communism, libertarian socialism, social anarchism and syndicalism. |
| Variations | Free market capitalism (also known as free market capitalism). laissez faire), state capitalism (also known as neo-mercantilism). | Socialism market, communism, state socialism, social anarchism. |
| Early exponents | The ideas of trade, buying and selling have existed since the beginning of civilization. Free market capitalism or laissez faire was brought to the world during the 18th century by John Locke and Adam Smith, seeking an alternative to feudalism. |
In 1516, Thomas More wrote in. Utopia about a society based on the common ownership of goods. In 1776, Adam Smith defended the labor theory of value, ignoring Kant’s view that prices are derived from supply and demand. |
| Worldview | Capitalists see market-based societies as symbols of freedom, priding themselves on allowing social and economic freedoms not experienced in the realm of communism and fascism. The focus is individualism as opposed to nationalism. |
Socialism is a movement of the worker and the middle class, all for a common democratic goal. |
Comparative infographic
Main characteristics of capitalism
- It is a market-based economy, composed of buyers (individuals) and sellers (private or corporate enterprises);
- The goods and services produced are intended to profit, and that profit is reinvested in the economy;
- Government should not interfere in free market economies, i.e., the market determines investments, production, distribution, and decisions;
- Government interference is only permitted in making and enforcing rules or policies governing the conduct of business;
- There is a need for production and purchasing continuous for a capitalist economy to function efficiently;
- Capitalists believe that government does not use economic resources efficiently as a private enterprise.
See also Modernity and postmodernity: characteristics and differences.
Main characteristics of socialism
- The means of production are owned by public or cooperative enterprises, and individuals are compensated on the principle of individual contribution;
- There is equal opportunity for all;
- Large-scale industries are cooperative endeavors and, therefore, the returns from those industries must be returned to and benefit society as a whole;
- Economic activity and production are planned by the central planning authority and based on human consumption needs and not on economic demands;
- Socialists believe that economic inequality is bad for society and the government is responsible for reducing it through programs that benefit the poor.
Advantages of capitalism
1. Consumer choice
Individuals choose what to consume, and that choice leads to more competition and better products and services.
2. Efficiency of the economy
Demand-driven goods and services create incentives to reduce costs and avoid waste.
3. Economic growth and expansion
This process increases gross national product (GNP) and raises living standards.
Advantages of socialism
1. Decreases inequality
In socialism, no individual can have much more than the other, and enterprises are owned by the government. Money is not a controlling factor in a socialist society.
2. Needs are met
Everyone’s needs must be met. This means that health care is universal, education is free, food is provided, as well as clothing and other necessities of life.
3. Mobilization of goods
Disasters of all types can occur at any time, and, when they do, an immense amount of services and goods are needed to ensure that everyone is safe and cared for.
In socialism, the government has full control of those goods and can easily mobilize them to the areas that need them most.
4. It has widely used ideas
The idea of socialism is used in virtually every country, in some form. It is the only way to ensure that some of the most basic and necessary things are provided to all people.
Examples of this are the public education system in the United States and universal health care in Canada.
Disadvantages of capitalism
Monopolies of power
Firms with monopoly power (when a specific person or firm is the sole supplier of a given commodity) can abuse their position by charging higher prices.
2. Inequality
A capitalist society is based on the right to pass on wealth to future generations.
If a small group of people retain all the wealth and that wealth continues to be passed on to the same groups of people, inequalities and social division occur.
3. Recession and unemployment
An economy based on the consumer and producer market can have many variations, such as recessions and unemployment.
Disadvantages of socialism
1. The historical failure
Throughout the world, several countries tried the idea of socialism, and all of them failed.
This is one of the biggest problems with socialism, the fact that it has been proven not to work, no matter how many different adjustments the government tries to apply.
2. Nothing is yours
Private property is forbidden in a socialist society. This means that you own nothing, since property belongs to “everyone” or to the government.
3. Less innovation and growth
With socialism, you have your basic needs taken care of, so you don’t have to worry about your meals or whether you have a house.
This may sound good, but it can make people comfortable, and with it innovation, creativity, motivation, and other forms of societal advancement diminish.
4. It is expensive
It costs a lot of money to provide everyone with the things they need, and that money has to come from somewhere.
So, all the money that is earned by citizens is taxed at huge percentages to cover all the costs.
See also:




