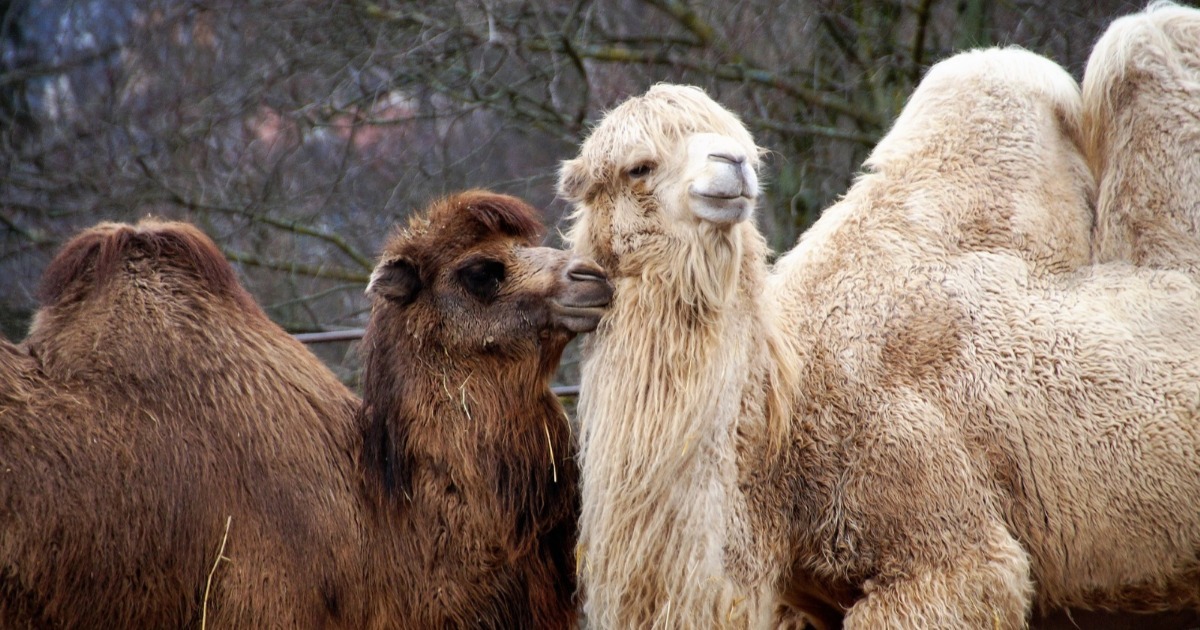
The camel and the dromedary are mammalian animals belonging to the order Artiodactyla or even-toed ungulates, i.e. with hooves. Both animals are two different species of the same genus:
- Camelus dromedarius: it is the dromedary of a humpback;
- Camelus bactrianus: it is the two-humped camel.
Both the camel and the dromedary have been domesticated by man, mainly for their ability to withstand the adverse climatic conditions of desert regions. They are used for milk, wool, meat and transport.
A mnemonic rule to remember which is the camel and which is the dromedary is:
- Dromedary begins with “D” which has only one hump.
- Bactrian camel begins with “B” which has two humps.
| Camel | Dromedary | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Camelus bactrianus | Camelus dromedarius |
| Common name | Bactrian camel | Arabian camel |
| Jorobas | Two: | One; store 36 kg of fat. |
| Location | Central Asia: China, Mongolia. | North Africa, West Asia, central Australia. |
| Height | 1,80-2,3 m. |
Male: 1.8-2 m. Female: 1.7-1.9 m. |
| Weight | 300-1000 kg. |
Male: 400-600 kg. Female: 300-540 kg. |
| Extremities | Shorter and more robust. | Longer and thinner. |
| Fur | Dark to light brown, thick hair on head, neck, humps, legs and tail. It can reach a length of 25 cm. | Brown, concentrated on shoulders, hump and neck. |
What is a camel
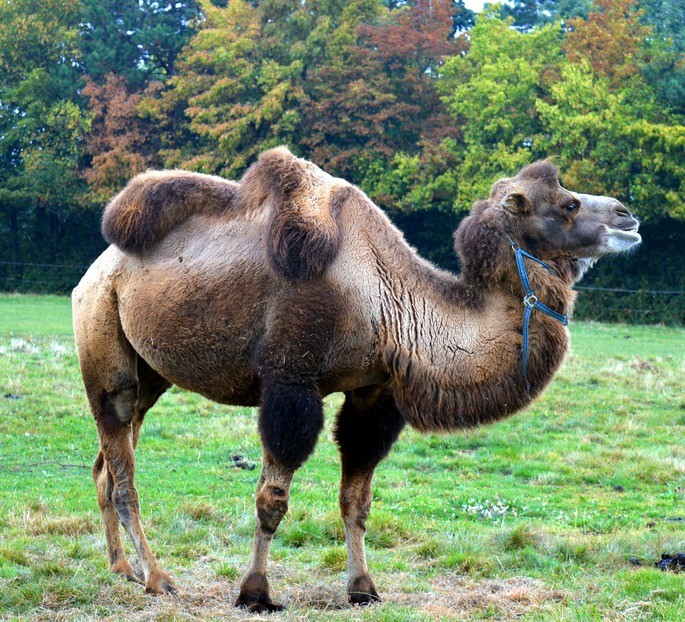

The camel is a more robust-bodied animal characterized by two humps. Its scientific name is Camelus bactrianus. The Bactrian camel is named after the ancient region of Bactria, where the domestication of this animal is believed to have begun.
Characteristics of the camel
- Two humps on the back: erect and full when food resources are available, drooping and empty when there are food deficiencies.
- More robust body.
- Thick, double lashes.
- Long hair, which increases during the winter and moults in the summer.
- Thicker limbs.
What is a dromedary
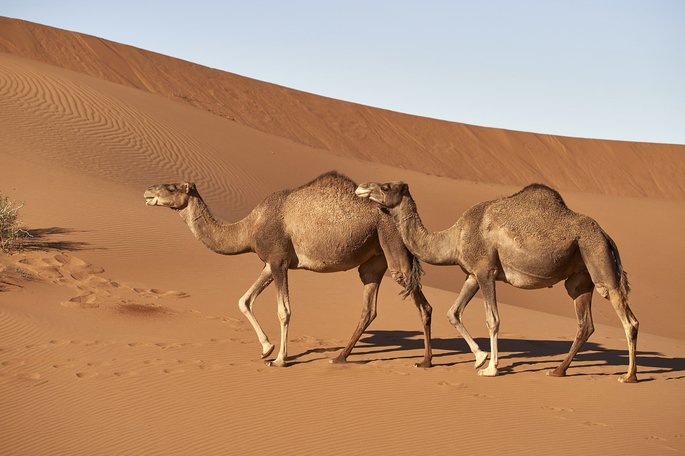

The dromedary is a large mammalian animal belonging to the family Camelidae, scientific name. Camelus dromedarius.
It shares the same genus as the camel, and is commonly known as the Arabian camel, as it is mainly found in North Africa, the Middle East and the Arabian Peninsula. In the 19th century, Australia imported dromedaries from India to enable them to travel in the country’s desert interior.
Dromedary characteristics
- A simple hump: 20 cm high, it is the fat store.
- Long curved neck.
- Narrower and taller body.
- Thick double eyelashes.
- The coat is brown long hair and concentrated on the throat, shoulders and hump.
- Strong, slender, long limbs, with two toes on each paw.
See also: Oviparous, viviparous and ovoviviparous animals.