Altitude and latitude are two magnitudes that allow to measure geographical distances.
Altitude, as applied to geography, refers to the vertical distance of any terrestrial point with respect to sea level.
Latitude, on the other hand, is a measure of distance between the equator and a terrestrial point.
| Altitude | Latitude | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Vertical distance between a point on the earth’s surface with respect to sea level. | Distance between a point on the earth’s surface with respect to the equator. |
| Unit of measurement | Meters above sea level (m.a.s.l.). | Degrees (°). |
| Measuring method. |
|
|
| Examples | Pico Orizaba, at 5,610 m.a.s.l., in Mexico. | Mexico City, latitude 19°25’42.5.5” N. |
What is altitude
The altitude is the distance measured by any point on the earth’s surface, taking as a reference the mean sea level, expressed in meters (m.a.s.l.).
It should be noted that meters above sea level is a measurement used almost everywhere in the world, with the exception of North America and the United Kingdom, where a measurement called foot (foot),which is equivalent to 30.48 centimeters.
On the other hand, altitude is measured vertically, hence it is confused with height and they are used as synonyms. However, altitude measures the vertical distance of a terrestrial point with respect to any reference point, not necessarily above sea level.
An example of a geographic area with a prominent elevation is the Pico Orizaba, the highest point in Mexico with an altitude of 5,610 m.a.s.l.
Altitude and meters above sea level
Due to the shape of the planet Earth and its geographical features, average sea levels vary and therefore, the altitudes of various regions are different.
In that sense, there are two ways to calculate mean sea level:
Orthometric altitude
It is the vertical distance of a terrestrial point with respect to the terrestrial geoid (theoretical surface of the Earth), and is determined by the intensity of the gravitational field at different points of the planet.
Ellipsoidal altitude
It is the vertical distance of a terrestrial point with respect to the terrestrial ellipsoid (it is a frame of reference of the shape of the Earth, but much simpler than the geoid). It is a measurement used in space geodesy.
Discrepancies between geoidal and ellipsoidal Earth models can lead to confusion or miscalculations. For this reason, the orthometric height is usually the measure used by official institutions in charge of measuring the national territory.
How altitude is measured
There are three methods for knowing the altitude of a point on the earth’s surface:
Use of altimeter
The altimeter is a precision instrument used in aviation and is used to determine the vertical distance between the ground point where it is located and a reference system. It is based on the relationship between atmospheric pressure and altitude (the lower the pressure, the higher the altitude).
Use of GPS
A global positioning system, or GPS, is a position sensing platform that works with a network of satellites.
When a GPS user requires to know an exact altitude, data from at least four satellites are collected and combined, resulting in a distance with a margin of error of up to five meters.
Digital Elevation Model
This is a graphic representation of a surface, very similar to 3D and elaborated from aerial or satellite digital photographs.
What is latitude
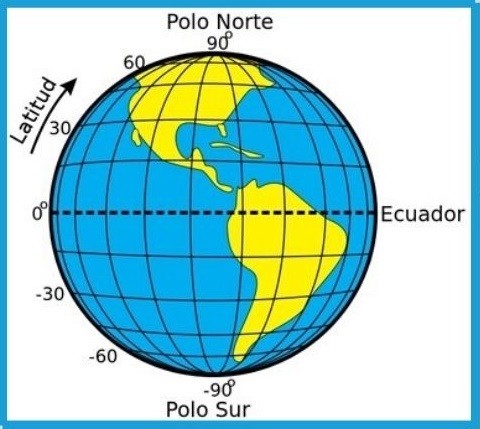
It is the distance that exists between any point on the earth’s surface with respect to the equator or zero parallel, expressed in degrees (°). Parallels are imaginary lines perpendicular to the earth’s axis that divide the earth into two major zones: the northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere.
As we will see below, parallels create three major latitudinal zones:
Polar zone
It is formed by the Arctic and Antarctic polar circle. It has a predominantly frigid climate due to the absence of sunlight for long periods of time. It is located between 66° and 90° latitude.
Temperate zone
It is located between the polar circles and the intertropical zone. The climate is polar, temperate and subtropical. It is located between 20° and 70° latitude.
Intertropical zone
It owes its name to its location, since it is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. It is a zone of great biodiversity, located between 30° north latitude and 30° south latitude.
You may be interested to see also Types of climate.
How latitude is measured
Latitude is obtained by knowing the angle formed by a straight line drawn from any point (P) to the polar axis, taking the equator as a reference.
The measurement obtained is expressed in degrees of latitude and can range from 0° (equator) to 90° (north) or -90° (south).
The degrees or tenths of a degree of an angle are also expressed in latitude, and are presented according to various systems. Using the latitude of Mexico City as an example, they would be:
- Simple decimal standard: 19.4284706
- Degrees decimal (GD): 19.4285° N
- Degrees and decimal minutes (GMD).: 19°25.708′ N
- Degrees, Minutes and Seconds (GMS): 19°25’42.5” N
See also: Parallels and meridians.
Latitude and longitude
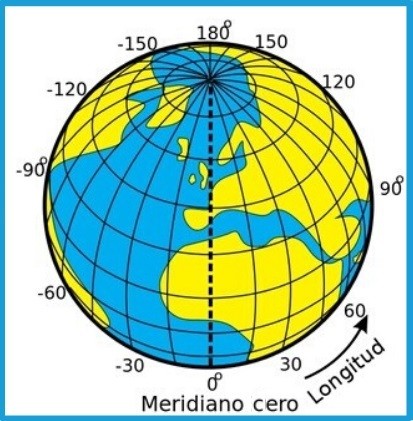
Longitude refers to the distance of any point on the earth’s surface from the zero meridian or Greenwich meridian, which divides the earth into eastern hemisphere (west), and western hemisphere (east).
Recall that meridians are imaginary lines in the shape of a semicircle that cross the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole.
The Earth’s surface has 360 meridians (180 in the east direction and 180 in the west direction). However, the main ones would be:
- Greenwich MeridianGreenwich Meridian: it is located in London. From it begins the counting of the rest of the meridians.
- Antimeridianis the meridian that is 180 degrees from the zero meridian. It crosses the Pacific Ocean.
The concept of longitude is almost always related to that of latitude because these two magnitudes are required in order to locate the coordinates of a place.
See also: