Methods of separation of mixtures are physical techniques used to separate the components of a mixture. A mixture can be homogeneous, when its components are indistinguishable to the naked eye, or heterogeneous, when differences between its components are evident.
The importance of these methods is that they allow us to obtain pure substances from their mixtures, without altering their chemical structure. For example, to obtain sea salt, evaporation is used to remove the water from the mixture.
|
Method of separation |
Definition |
Type of mix |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filtration | Separation of components solids from a liquid mixture |
Heterogeneous | Coffee ground coffee filtering |
| Sieving | Separation of particles according to size through a sieve. | Heterogeneous | Sifting of flour for desserts |
| Sedimentation | Deposition of suspended particles in a mixture by the action of gravity. | Heterogeneous | Wastewater treatment |
| Decantation | Transferring a liquid from a container to another |
Heterogeneous | Separation of sediments from wine |
| Distillation | Separation of components with different boiling points |
Homogeneous | Distillation of water to remove impurities. |
| Evaporation | Solvent removal from a mixture |
Homogeneous | Obtaining organic extracts dissolved in alcohol. |
| Immantation | Separation of components by their magnetic property |
Heterogeneous | Obtaining iron filings in a mixture with sand. |
| Chromatography | Separation of components by their affinity to a mobile phase and a fixed phase. | Homogeneous Heterogeneous |
Separation of plant pigments in a paper. |
| Centrifugation | Separation based on centrifugal force | Heterogeneous | Separation of red blood cells from blood plasma. |
| Crystallization | Promote the formation of crystals | Homogeneous | Formation of sugar crystals from a sugar-water mixture. |
| Electrophoresis | Separation based on difference in electrical charge | Homogeneous | Protein separation |
| Sublimation | Passing a solid to gas without passing through liquid. | Heterogeneous | Separation of iodine from sand |
1. Filtration
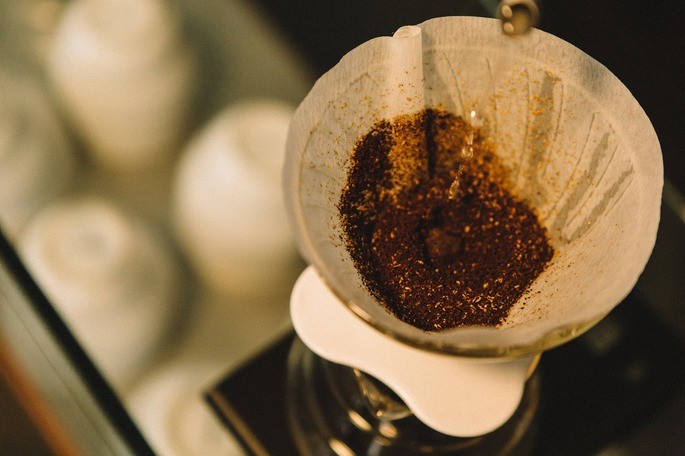

Filtration consists of passing a heterogeneous liquid-solid mixture through a material that retains the solid and allows the liquid to pass through. For example, we use a filter to separate the mixture of ground coffee and liquid coffee.
Filters can be made of different materials, whose main characteristic is that it must be porous. For example, a mixture of coagulated milk is passed through a fine cloth, separating the whey from the milk solid, which is how cheese is made.
2. Sifting
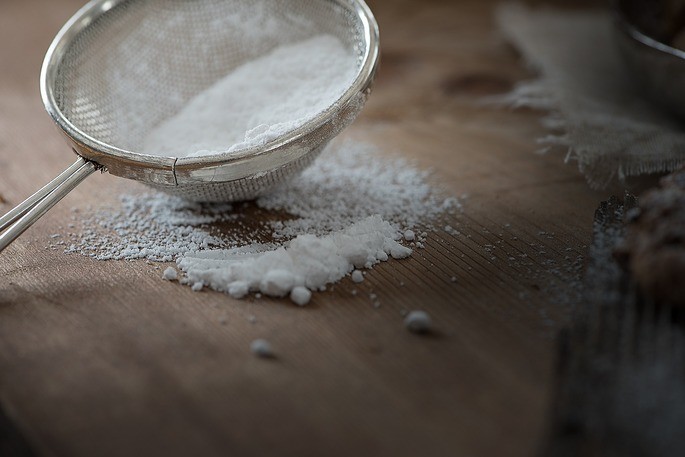

Sieving is the method of separating mixtures with solid components with different sizes, which pass through a strainer or sieve.
Sifting is used to remove lumps of flour and use the finer flour for baking. It is also used in construction, separating fine sand from pebbles.
3. Sedimentation
Sedimentation is the method that separates the solid components of a liquid mixture by the effect of gravity.
This method is used in wastewater or sewage treatment plants by letting the solid waste settle, i.e., fall to the bottom.
4. Decanting
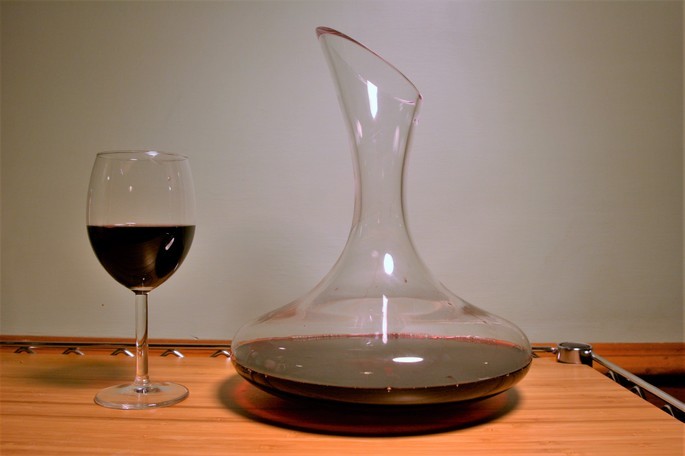

This method consists of transferring a liquid from one container to another. It is applied to separate heterogeneous solid-liquid mixtures, such as water and sand, or liquid-liquid mixtures that do not mix with each other, such as water and oil or water and gasoline.
In the chemistry laboratory, a separatory funnel is used, which facilitates the separation of liquids, because it has a stopcock at the bottom.
For example, decanting is used to separate red wine from the sediment that settles to the bottom of the bottle.
5. Distillation
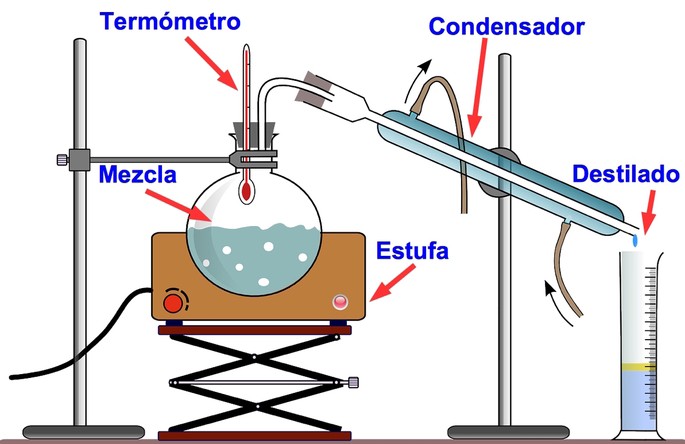
Distillation is the process that separates the components of a liquid mixture, based on the difference in temperature that each one passes to the gaseous state. The distillation equipment allows the gas to be returned to the liquid state by means of condensers.
For example, water boils at 100 ºC while alcohol boils at 78.37 ºC. When a mixture of alcohol and water is heated above 78 ºC, the alcohol becomes a gas and rises, passing to the condenser and dripping at the end into a collecting vessel.
Distilleries are factories where distillations are made on a large scale, usually to concentrate the alcohol level of fruit fermentates, to produce liquors, spirits, rums, among others. In the past, this process was carried out in copper stills.
Gasoline and other petroleum derivatives are obtained through fractional distillation. This process is carried out in oil refineries.
6. Evaporation
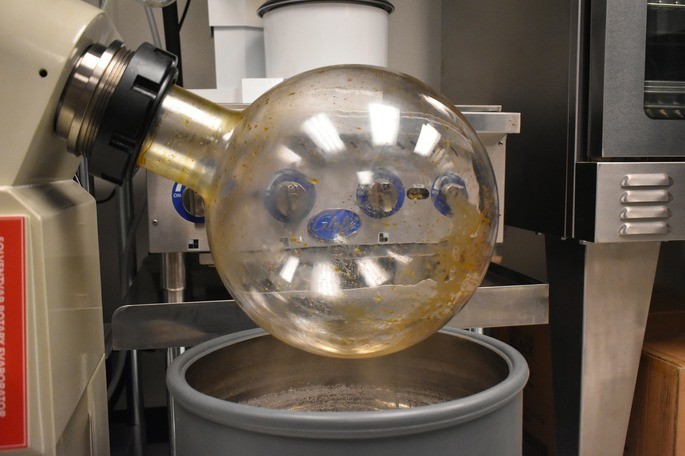

Evaporation is a physical separation method based on evaporating the liquid in which the substances are dissolved. It is mainly used in chemistry, when organic substances are extracted by means of solvents such as acetone, ethanol or hexane. These are liquids with low boiling points, so they evaporate at low temperatures.
7. Immantation

Magnetization is the method of separating heterogeneous mixtures based on trapping components that are attracted by a magnet.
Some laboratories have designed proteins attached to magnetic particles, which serve to separate them using magnets.
8. Chromatography
Chromatography is a method of separation of homogeneous or heterogeneous mixtures. It is based on the difference in velocity of a substance between two phases: a mobile phase and a fixed phase. The mobile phase moves by dragging the different components of the mixture, which separate as they collide with the fixed phase.
The fixed phase can be a solid such as paper, a gel such as agar, or a liquid such as acetonitrile. The mobile phase can be liquid or gas. Depending on this, we have thin layer chromatography, liquid chromatography, and gas chromatography.
9. Centrifugation
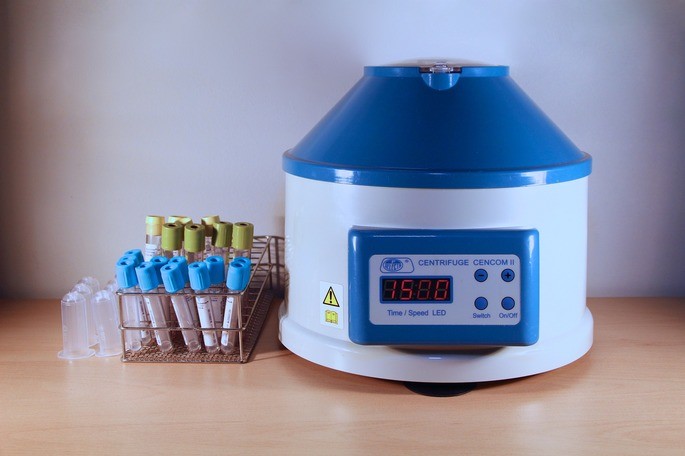

Centrifugation is a method of separation of liquid heterogeneous mixtures based on centrifugal force. This force originates when a body rotates and tends to move away from the axis of rotation. This separates the denser components of a mixture from the less dense ones. For example, blood cells are separated from plasma using centrifugation.
Centrifuges are devices that rotate at high speed, in which the samples to be separated are placed. They are widely used in clinical laboratories and in research.
10. Crystallization
Crystallization is a method for separating homogeneous mixtures of a solid with a liquid. It consists of promoting the formation of crystals with ordered structures. This can be achieved in several ways: by cooling a solution, evaporating the solvent or adding a different solvent.
Crystallization is observed when a solution is saturated with salt in boiling water and then allowed to cool.
11. Electrophoresis
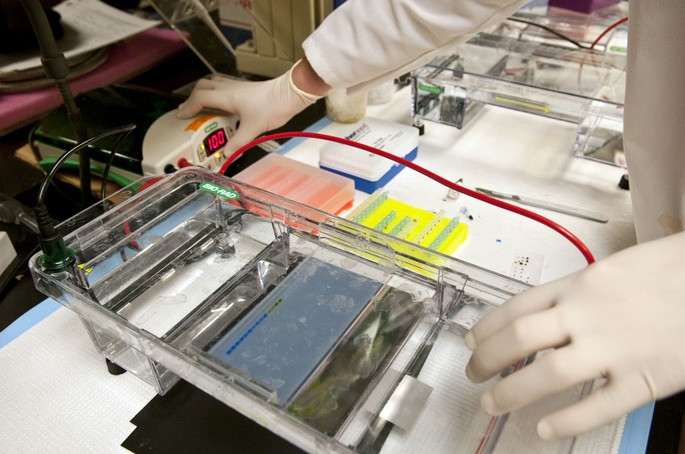

Electrophoresis is the separation technique based on the electrical charge of substances present in a mixture. It consists of placing the mixture and passing an electric current through it, so that the positively charged substances move to the negative pole, while the negatively charged substances move to the positive pole.
This technique is fundamental in the analysis of biological samples and is used to separate proteins and nucleic acids, among other compounds. For example, lipoproteins in blood plasma can be separated by electrophoresis to measure their cholesterol content and assess the risk of cardiovascular disease.
12. Sublimation
Sublimation is the change from a solid to a gas without passing through the liquid state. Sublimation is used to separate mixtures of organic compounds, where one of the compounds can sublimate.
For example, in a mixture of sand and iodine, the iodine can be separated by heating it. It passes to the gaseous state by rising and when it passes through a cold surface it solidifies again.
See also:




