The primary, secondary and tertiary sectors are the main categories of economic activities in a country.
The primary sector encompasses activities related to obtaining natural resources, such as agriculture and fishing.
The secondary sector or industrial sector is in charge of the transformation of resources coming from the primary sector, such as the textile and automobile industries.
The tertiary sector covers the provision of services, such as commerce.
The level of economic development of a country is related to the prevailing sectors. For example, in developing or underdeveloped countries, the majority of people able to work are concentrated in the primary sector. Meanwhile, in societies with a high level of development, the tertiary sector predominates, followed by the secondary sector.
This classification was established between 1930 and 1940 by Alan Fisher and Colin Clark to facilitate comparison between countries and how their economies evolve.
| Sector Primary |
Sector Secondary |
Sector Tertiary |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic sector encompassing activities for obtaining resources from nature. | Area of the economy where the transformation of raw materials into processed products takes place. | Sector of activities that are responsible for distributing and trading goods and services. |
| Geographic space | Depends on geography and climate. | Independent of geography. | Independent of geography. |
| Resources | Linked to nature | Coming from the primary sector | From the secondary sector |
| Activities |
Cultivation, harvesting, extraction and obtaining raw material. |
|
|
| Population employed | Rural areas | Rural or urban areas | Urban areas |
| Examples |
Corn crop Raising cows Capture fishing Logging of forests for timber |
Automobile assembly Real estate construction Manufacture of fabrics and clothing Bottled beverage production |
Hairdressers Restaurants Clinics and hospitals Stores and offices |
Primary sector
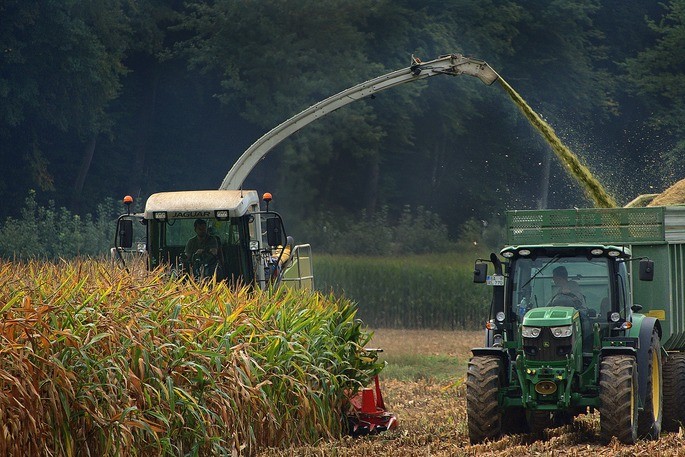

The primary sector is the sector of the economy that groups all those activities related to the extraction of natural resources. It is in charge of providing food for the population and the raw material to be used in the secondary sector.
Generally speaking, developing countries depend mainly on their primary activities, mainly agriculture, while developed countries employ less labor in this sector. For example, in Mexico, the cultivation of corn and sugarcane accounted for more than 50% of production in 2019.
The primary sector is characterized by by:
- Depend on geography and climateThe activities that can be carried out in the primary sector are determined by location and climate. For example, mango cultivation is limited to tropical areas, while apples are grown in temperate regions.
- Being linked to natureresources are obtained directly from nature. For example, fishing takes place in seas, oceans or rivers, while agricultural products come from the soil.
- Develop activities for obtaining raw materials.These include the cultivation of plants for the collection of fruits, vegetables, wood, fibers, extraction of animals for the production of meat and leather, milk and derivatives.
- To be developed by the rural population: primary sector activities are concentrated in the countryside where the population is low and less educated.
Examples of primary sector activities are:
- Agriculture: cultivation of corn for human and animal feed, cultivation of olives for oil, cultivation of cotton for cloth.
- Livestock: raising cows for milk and cheese production, raising sheep for wool production.
- Fishing: capture, trawling, open sea, tuna fishing, salmon farming.
- Logging: cedar cultivation for timber, hemp cultivation for paper, pine cultivation for furniture.
You may also be interested in:
Secondary sector
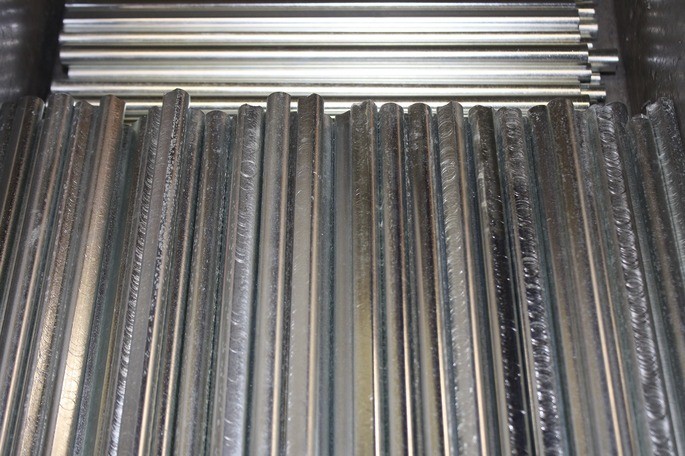

The secondary sector comprises economic activities involving the transformation of raw materials into processed products, energy production and construction. This is done through industrial processes that require energy and can be established in any region.
Mining is classified within the secondary sector, although it sometimes fits into the primary sector because it is an extractive activity.
In general, underdeveloped countries occupy less than 20% of their population in the secondary sector. Among the most industrialized countries are China, South Korea, Hong Kong, Malaysia, India and Taiwan in Asia, the United States, Mexico, Chile and Brazil in America, Germany and Switzerland in Europe.
The secondary sector is characterized by by:
- Being independent of geographical area or climate: factories can be set up almost anywhere, in the countryside, in the cities or on the outskirts of cities. In other words, an automobile factory can be located in any physical space where raw materials arrive to be transformed.
- Develop in both rural and urban areas.activities can be carried out in urban areas, where small factories are located, or in rural areas.
- Transforming raw materialsmilk is transformed into cheese or butter in cheese factories, cotton is transformed into yarns and fabrics.
- To be automatableindustrialization allows many of the activities in this sector to be carried out by machines, speeding up and improving production efficiency.
Examples of secondary sector activities:
- Petroleum industry: exploitation, refining, pipelines and storage of petroleum and petroleum products, petrochemicals.
- Textile industry: looms, garment factory, yarn manufacturing.
- Automotive industry: assembly lines, engine complex and foundries
- Electronics industry: assembly of electronic equipment and household appliances, medical equipment, measuring instruments.
You may be interested to see also Developed countries and underdeveloped countries.
Tertiary sector
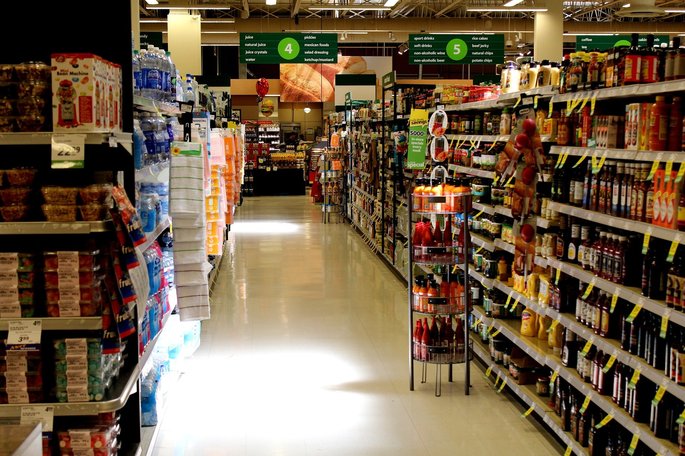

The tertiary sector groups economic activities related to the distribution and marketing of products produced by the secondary sector and the provision of services to the consumer. In other words, this sector offers products and goods at the last stage of production.
Unlike the primary and secondary sectors, the tertiary sector is a very heterogeneous group of activities. These include hairdressers, doctors, shopkeepers, street sweepers, among others.
The tertiary sector is predominant in developed countries. For example, in Spain, more than 60% of the working population will be in the service sector from 2008 to 2021.
The tertiary sector is characterized by by:
- To be independent of the geographical area: the geographical location does not determine the performance of activities in this sector.
- Concentrate in urban areas: as the activity to offer services to the population
- To market finished productssalespeople promote the products to the consumer.
- Providing servicespeople with or without special training offer to perform certain activities for other people, e.g. a hairdresser performs haircuts or hairstyles in exchange for payment.
Examples of tertiary sector activities:
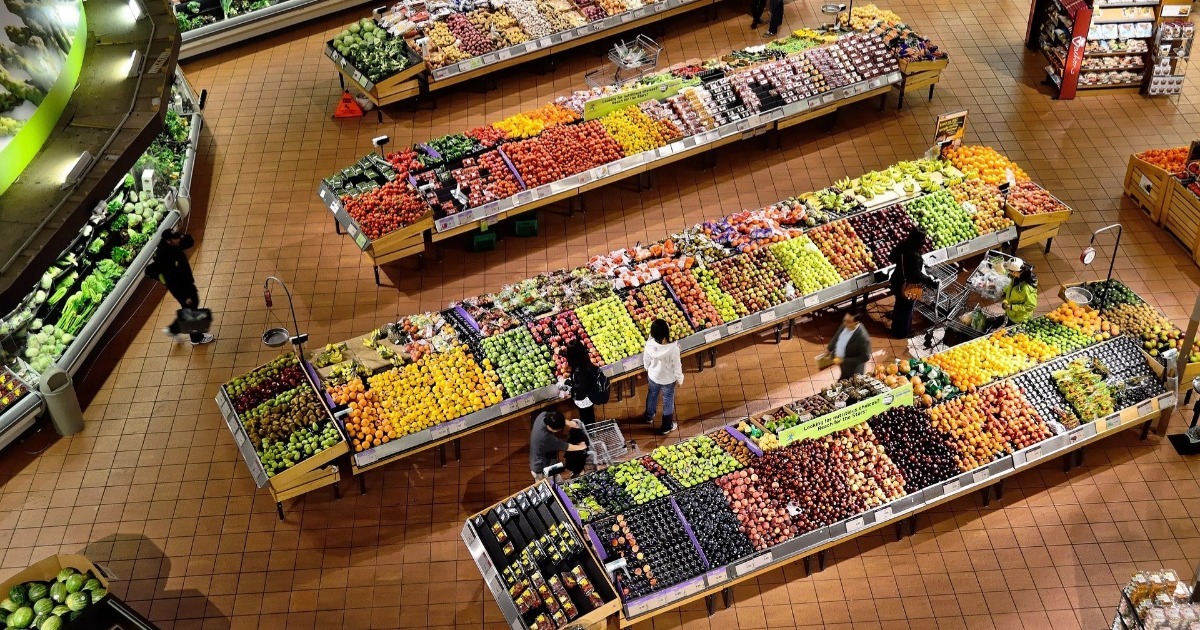
- Commerce: shopping malls, supermarkets, bookstores, stores.
- Transportation: airports, ports, bus terminals.
- TourismTravel agencies, hotels and resorts,
- Financial services: banks, exchange houses, insurance companies.
- Health serviceshospitals, clinics, ophthalmology, dentistry,
- Entertainment services: theater, cinema, amusement parks.
You may also be interested to see:
References
Aguilera Arilla, M.J., Borderías U., M.P., González Y., M.P., Santos P., J.M. (2010) Geografía General II: Geografía Humana. National University of Distance Education. Madrid.
Bjelland, M.D., Montello, D.R., Getis, A. (2020) Human Geography: Landscapes of human activities 13 ed. McGraw-Hill Education. New York.